A sort based around sorting values into values smaller and larger than a pivot point.
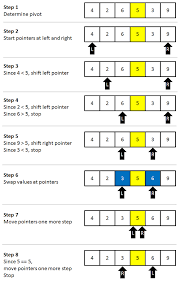
It is recursive, repeating until handling a list/segment of one.
Explanation
Info
To explain.
Implementation
from random import randint
data = [randint(1, 100) for x in range(10)]
# utility functions
def swap(from_pos: int, to_pos: int, arr: list[int]) -> None:
arr[from_pos], arr[to_pos] = arr[to_pos], arr[from_pos]
# recursive implementation
def quick_sort(start: int, end: int, arr: list[int]) -> None:
if start < end:
pivot = partition(start, end, arr)
quick_sort(start, pivot - 1, arr)
quick_sort(pivot + 1, end, arr)
def partition(start: int, end: int, arr: list[int]) -> int:
pivot = arr[end]
pointer = start - 1
for i in range(start, end):
if arr[i] <= pivot:
pointer += 1
swap(pointer, i, arr)
swap(pointer + 1, end, arr)
return pointer + 1
print(data)
quick_sort(0, len(data) - 1, data)
print(data)Simple Example
from random import randint
data = [randint(1, 100) for x in range(10)]
# utility functions
def swap(from_pos: int, to_pos: int, arr: list[int]) -> None:
arr[from_pos], arr[to_pos] = arr[to_pos], arr[from_pos]
# recursive implementation
def quick_sort(arr: list[int]):
if len(arr) > 1:
pivot = arr[0]
left = [x for x in arr[1:] if x <= pivot] # ignoring first (pivot), select all of less/equal value
right = [x for x in arr[1:] if x > pivot] # ignoring first (pivot), select all of greater value
quick_sort(left) # sort the array
quick_sort(right)
arr.clear()
arr.extend(left) # restructure the array
arr.append(pivot)
arr.extend(right)
quick_sort(data)
print(data)Warning
This example does not demonstrate the fundamental process of quick sort and rather abstracts it to a much more simple concept.
Advantages
- Fast on large datasets
- O(n log n) best case scenario speed
- O(1) space
- If partitioning, not creating new arrays like in Simple Example
Disadvantages
- O(n2) worst case scenario speed
- Negligible speed benefits on small datasets