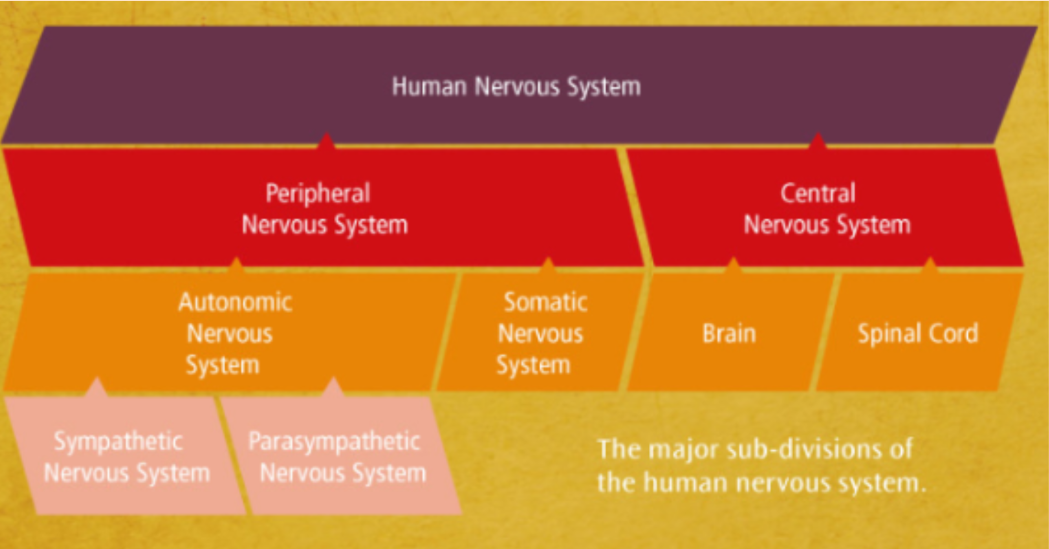
Types
- Central (CNS)
- Brain and spinal cord
- Receives and processes information from sensory receptors
- Spinal cord relays information between the brain and rest of the body
- Peripheral (PNS)
- All nerves
- Relays information from the CNS to the rest of the body
Functionality
- To collect, process and respond to information in the environment
- To coordinate the working of different organs and cells in the body
Structure
Central Nervous System
Brain
- Controls higher mental functions, conscious awareness and decision making
- Receives information from sensory receptors
- Sends message to the muscles and glands through the spine
Spinal Cord
- Relay information between the brain and nerves in the rest of the body
- Also contains nerve cells which do not require involvement from the brain
- Responsible for reflex actions
Peripheral Nervous System
- Transmits information to and from the central nervous system
- Two sub-parts are the autonomic system and the somatic system
Somatic Nervous System
Functions
- Controls muscle movements
- Responsible for nearly all external voluntary muscle movements
- Receives messages from sensory receptors and carries sensory information to the brain/CNS
- Responsible for processing sensory information via. external stimuli (hearing, touch and sight)
Autonomic Nervous System
- Carries out actions without conscious awareness
- Responsible for controlling automatic involuntary physiological processes internally
Functions
- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Digestion
- Sexual arousal
- Stress responses
Sympathetic Nervous System
Functions
- Increases heart rate
- Increases breathing rate
- Dilates pupils
- Inhibits digestion
- Inhibits saliva production
- Contracts rectum
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Function
- Decreases heart rate
- Decreases breathing rate
- Constricts pupils
- Stimulates digestion
- Stimulates saliva production
- Relaxes rectum
